History Of Jerusalem During The Early Muslim Period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
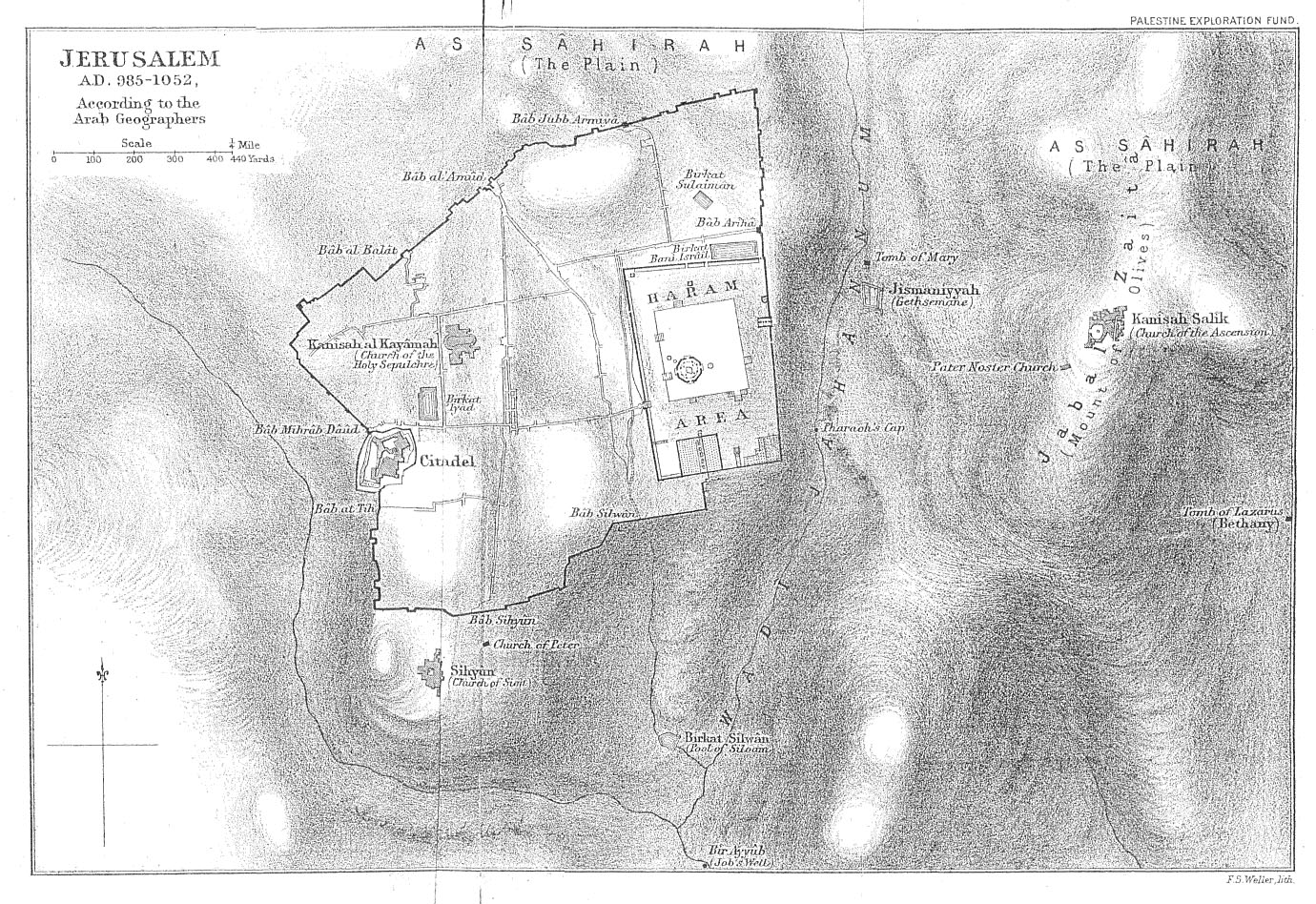 The history of Jerusalem during the Early Muslim period covers the period between the capture of the city from the
The history of Jerusalem during the Early Muslim period covers the period between the capture of the city from the
 The Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik (), who had served as the governor of Jund Filastin under his father Caliph
The Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik (), who had served as the governor of Jund Filastin under his father Caliph
Jerusalem: Under the Arabs
/ref>
 The history of Jerusalem during the Early Muslim period covers the period between the capture of the city from the
The history of Jerusalem during the Early Muslim period covers the period between the capture of the city from the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
s by the Arab Muslim armies of the nascent Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
in 637–638 CE, and its conquest by the European Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
armies of the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
in 1099. Throughout this period, Jerusalem remained a largely Christian city with smaller Muslim and Jewish communities. It was successively part of several Muslim states, beginning with the Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of t ...
caliphs of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
, the Umayyads Umayyads may refer to:
*Umayyad dynasty, a Muslim ruling family of the Caliphate (661–750) and in Spain (756–1031)
*Umayyad Caliphate (661–750)
:*Emirate of Córdoba (756–929)
:*Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ( ar, خ ...
of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
and their nominal Turkish vassals in Egypt, and the Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dy ...
caliphs of Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, who struggled over it with the Turkic Seljuks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
and different other regional powers, only to finally lose it to the Crusaders.
The second caliph, Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate o ...
(), secured Muslim control of the city from the Patriarch of Jerusalem. During his rule Muslim prayer was likely established on the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compoun ...
and limited numbers of Jews were allowed to reside in the city after a several centuries-long ban by the Romans/Byzantines. Beginning with Caliph Mu'awiya I
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
(), the early Umayyad caliphs devoted special attention to the city as a result of its sanctity and several obtained their oaths of allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For ...
there. The Umayyads Abd al-Malik () and al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ( ar, الوليد بن عبد الملك بن مروان, al-Walīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān; ), commonly known as al-Walid I ( ar, الوليد الأول), was the sixth Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad ca ...
() invested considerably in constructing Muslim edifices on the Temple Mount, namely the Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
and the al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situate ...
, as well other religious and administrative structures, gates
Gates is the plural of gate, a point of entry to a space which is enclosed by walls. It may also refer to:
People
* Gates (surname), various people with the last name
* Gates Brown (1939-2013), American Major League Baseball player
* Gates McFadde ...
, and roadworks. Their successor Sulayman
Sulayman (Arabic: سُلِيمَان ''sulaymān'') is an Arabic name of the Biblical king and Islamic prophet Solomon meaning "man of peace", derived from the Hebrew name Shlomo.
The name Sulayman is a diminutive of the name Salman (سَلْ ...
() likely resided in Jerusalem at the beginning of his reign, but his founding of the nearby city of Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
came at the political and economic expense of Jerusalem in the long term.
Overview
Throughout the Early Muslim and Crusader periods, up until Saladin's conquest of 1187, Jerusalem retained a sizable Christian majority, which only ceased to exist once Saladin removed the Frankish population in 1187. During the early centuries of Muslim rule, especially under the Umayyad (661–750) andAbbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
(750–969) dynasties, the city prospered; the 10th-century geographers Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
and al-Istakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', fa, استخری, i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. - d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel-author and geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arab ...
describe it as "the most fertile province of Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
", while its native son, geographer al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
(born 946) devoted many pages to its praises in his most famous work, ''The Best Divisions in the Knowledge of the Climes''. Jerusalem under Muslim rule, however, did not achieve the political or cultural status enjoyed by the capitals Damascus, Baghdad, Cairo etc.
With the decline of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
, which split up in 888, a period of anti-Christian persecution by the Muslims began. However, the recovered Byzantines filled this void and as the Empire expanded under the Byzantine Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, Christians were again allowed to make pilgrimages to Jerusalem.
Rashidun period (630s–661)
Domination of the countryside
SouthernPalestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
was conquered by the Muslims under the commander Amr ibn al-As
( ar, عمرو بن العاص السهمي; 664) was the Arab commander who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and was assigned impor ...
following their decisive victory over the Byzantines at the Battle of Ajnadayn
The Battle of Ajnadayn ( ar, معركة أجنادين) was fought in July or August 634 ( Jumada I or II, 13 AH), in a location close to Beit Guvrin in present-day Israel; it was the first major pitched battle between the Byzantine (Roman) ...
, likely fought at a site about south-southwest of Jerusalem, in 634. Although Jerusalem remained unoccupied, the 634 Christmas sermon of Patriarch Sophronius of Jerusalem
Sophronius ( grc-gre, Σωφρόνιος; ar, صفرونيوس; c. 560 – March 11, 638), called Sophronius the Sophist, was the Patriarch of Jerusalem from 634 until his death. He is venerated as a saint in the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Ch ...
indicated that the Muslim Arabs were in control of the city's environs by then, as the Patriarch was unable to travel to nearby Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
for the ritual Feast of the Nativity due to the presence of Arab raiders. According to one reconstruction of the Islamic tradition, a Muslim advance force was sent against Jerusalem by Amr ibn al-As on his way to Ajnadayn. By 635 southern Syria was in Muslim hands, except for Jerusalem and the Byzantines' capital of Palestine, Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
. In his homily
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ex ...
of the Theophany
Theophany (from Ancient Greek , meaning "appearance of a deity") is a personal encounter with a deity, that is an event where the manifestation of a deity occurs in an observable way. Specifically, it "refers to the temporal and spatial manifest ...
(Orthodox Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany season, or Epiph ...
), , Sophronius lamented the killings, raids, and destruction of churches by the Arabs.
Siege and capitulation
It is unclear when Jerusalem was precisely captured, but most modern sources place it in the spring of 637. In that year the troops ofAbu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah
ʿĀmir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Jarrāḥ ( ar, عامر بن عبدالله بن الجراح; 583–639 CE), better known as Abū ʿUbayda ( ar, أبو عبيدة ) was a Muslim commander and one of the Companions of the Islamic prophet M ...
, head commander of the Muslim forces in Syria, besieged the city. The Muslim traditions hold that Caliph Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate o ...
(), who was headquartered in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
, made one or several visits to Jabiya
Jabiyah ( ar, الجابية / ALA-LC: ''al-Jābiya'') was a town of political and military significance in the 6th–8th centuries. It was located between the Hawran plain and the Golan Heights. It initially served as the capital of the Ghassanids ...
, the Muslims' principal camp in Syria, in 637–638. The modern historians Fred Donner and Hugh N. Kennedy
Hugh Nigel Kennedy (born 22 October 1947) is a British medieval historian and academic. He specialises in the history of the early Islamic Middle East, Muslim Iberia and the Crusades. From 1997 to 2007, he was Professor of Middle Eastern Histor ...
assess that he came to address multiple administrative matters in the newly conquered province. While in Jabiya, Umar negotiated Jerusalem's surrender with a delegation from the city, as the Patriarch insisted on surrendering to the Caliph directly rather than his commanders.
The earliest known Muslim tradition of Jerusalem's capture was cited in the history of al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري) was a 9th-century Muslim historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and ...
(d. 892) and credits the Arab commander Khalid ibn Thabit al-Fahmi for arranging the city's capitulation with terms guaranteeing Muslim domination of the countryside and safeguarding the city's inhabitants in return for tributary payment. Khalid ibn Thabit had been dispatched by Umar from Jabiya. The historian Shelomo Dov Goitein
Shelomo Dov Goitein (April 3, 1900 – February 6, 1985) was a German-Jewish ethnographer, historian and Arabist known for his research on Jewish life in the Islamic Middle Ages, and particularly on the Cairo Geniza.
Biography
Shelomo Dov (Fritz ...
considered this tradition to be the most reliable narrative of Jerusalem's capture. Another account, that contained in the histories of al-Ya'qubi
ʾAbū l-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer and perhaps the first historian of world cult ...
(d. 898) and Eutychius of Alexandria
Eutychius of Alexandria (Arabic: ''Sa'id ibn Batriq'' or ''Bitriq''; 10 September 877 – 12 May 940) was the Melkite Patriarch of Alexandria. He is known for being one of the first Christian Egyptian writers to use the Arabic language. H ...
(d. 940), holds that a treaty was agreed between the Muslims and Jerusalem's inhabitants, though the terms were largely the same as those cited by al-Baladhuri. The 10th-century history of al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
, citing the 8th-century historian Sayf ibn Umar
}) was an 8th-century Islamic historian and compiler of reports who lived in Kufa. He wrote the ('The Great book of Conquests and Apostasy Wars'), which was the later historian al-Tabari's (839–923) main source for the Ridda wars and the early ...
, reproduces the capitulation agreement in detail, though parts of it may have been altered from the time it was made. Although Goitein considered Sayf's account "worthless" on account of Sayf's general unreliability, the historians Moshe Gil
Moshe Gil ( he, משה גיל; February 8, 1921 – January 23, 2014) was an Israeli historian.
Academic career
Moshe Gil specialized in the historical interaction between Islam and the Jews, including the history of Palestine under the Islami ...
and Milka Levy-Rubin have argued that the tradition was largely authentic. The agreement for Jerusalem was generally favorable for the city's Christian inhabitants, guaranteeing the safety of their persons, their property, and churches, and allowing them the freedom of worship in return for payment of the ''jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
'' (poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
). Byzantine troops and other residents seeking to evacuate the city were given security assurances from the time they left Jerusalem until they reached their point of departure from Palestine. Gil assessed that Umar adopted a lenient approach so that the inhabitants could continue their way of life and work and thus be able to subsidize the Arab tribesmen garrisoned in Palestine.
The treaty cited in al-Tabari, and later Christian sources, contained a stipulation barring Jewish residency alongside the city's Christians, a continuation of a ban started in the days of Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
() and renewed in the days of Emperor Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
(). Among them was the history of Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian ( ar, ميخائيل السرياني, Mīkhaʾēl el Sūryani:),( syc, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܣܽܘܪܝܳܝܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Sūryoyo), died 1199 AD, also known as Michael the Great ( syr, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܪܰܒ݁ܳܐ, ...
(d. 1199), who wrote that Sophronius negotiated the ban on Jews residing in Jerusalem. ( see below).
Several later Muslim and Christians accounts, as well as an 11th-century Jewish chronicle, mention a visit to Jerusalem by Umar. One set of accounts held that Umar was guided by Jews who showed him the Temple Mount. Goitein considers the stories of Umar's visit to the city to be legendary. In the Muslim accounts, a prominent Jewish convert to Islam, Ka'b al-Ahbar, recommended that Umar pray behind the Holy Rock so that both ''qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the s ...
s'' (direction point of Islamic prayer) lay behind him. Umar rejected the suggestion, insisting that the Ka'aba
The Kaaba (, ), also spelled Ka'bah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah ( ar, ٱلْكَعْبَة ٱلْمُشَرَّفَة, lit=Honored Ka'bah, links=no, translit=al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah), is a building at the c ...
in Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
was the sole ''qibla''; Jerusalem had been the original ''qibla'' of the early Muslims until Muhammad changed it to the Ka'aba. The Muslim and Jewish sources reported that the Temple Mount was cleaned by the Muslims of the city and its district and a group of Jews. The Jewish account further noted that Umar oversaw the process and consulted with Jewish elders; Gil suggests the Jewish elders may be a reference to Ka'b al-Ahbar. The Christian accounts mentioned that Umar visited Jerusalem's churches, but refused to pray in them to avoid setting a precedent for future Muslims. This tradition may have been originated by later Christian writers to promote efforts against Muslim encroachments on their holy places.
Post-conquest administration and settlement
Jerusalem is presumed by Goitein and the historian Amikam Elad to have been the Muslims' main political and religious center inJund Filastin
Jund Filasṭīn ( ar, جُنْد فِلَسْطِيْن, "the military district of Palestine") was one of the military districts of the Umayyad and Abbasid province of Bilad al-Sham (Levant), organized soon after the Muslim conquest of the Leva ...
(district of Palestine) from the conquest until the foundation of Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
at the beginning of the 8th century. It may have been preceded by the Muslims' principal military camp at Emmaus Nicopolis
Nicopolis ( grc-gre, Νικόπολις, ''Nikópolis'') was the name of Emmaus ( he, אמאוס; grc-gre, Ἀμμαοῦς, ''Ammaoûs''; ar, عِمواس, ''Imwas'') under the Roman Empire until the conquest of Palestine by the Rashidun Calip ...
before this was abandoned due to the Plague of Amwas The plague of Amwas ( ar, طاعون عمواس, ''ṭāʿūn ʿAmwās''), also spelled plague of Emmaus, was a bubonic plague epidemic that afflicted Islamic Syria in 638–639, during the first plague pandemic and toward the end of the Muslim co ...
in 639. The historian Nimrod Luz, on the other hand, holds that the early Muslim tradition indicates Palestine from the time of Umar had dual capitals at Jerusalem and Lydda
Lod ( he, לוד, or fully vocalized ; ar, اللد, al-Lidd or ), also known as Lydda ( grc, Λύδδα), is a city southeast of Tel Aviv and northwest of Jerusalem in the Central District of Israel. It is situated between the lower Shephe ...
, each city having its own governor and garrison. An auxiliary force of tribesmen from Yemen was posted in the city during this period. Amr ibn al-As launched the conquest of Egypt from Jerusalem in , and his son Abd Allah transmitted hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
s about the city.
Christian leadership in Jerusalem entered a state of disorganization following the death of Sophronius , with no new patriarch appointed until 702. Nonetheless, Jerusalem remained largely Christian in character throughout the early Islamic period. Not long after the conquest, possibly in 641, Umar allowed a limited number of Jews to reside in Jerusalem after negotiations with the Christian leadership of the city. An 11th-century Jewish chronicle fragment from the Cairo Geniza
The Cairo Geniza, alternatively spelled Genizah, is a collection of some 400,000 Jewish manuscript fragments and Fatimid administrative documents that were kept in the '' genizah'' or storeroom of the Ben Ezra Synagogue in Fustat or Old Cairo, Eg ...
indicated that the Jews requested the settlement of two hundred families, the Christians would only accept fifty, and that Umar ultimately decided on the settlement of seventy families from Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Fo ...
. Gil attributed the Caliph's move to his recognition of the Jews' local importance, by dint of their considerable presence and economic strength in Palestine, as well as a desire to weaken Christian dominance of Jerusalem.
At the time of the conquest, the Temple Mount had been in a state of ruin, the Byzantine Christians having left it largely unused for scriptural reasons. The Muslims appropriated the site for administrative and religious purposes. This was likely due to a range of factors. Among them was that the Temple Mount was a large, unoccupied space in Jerusalem, where the Muslims were restricted by the capitulation terms from confiscating Christian-owned property in the city. Jewish converts to Islam may have also influenced the early Muslims regarding the site's holiness, and the early Muslims may have wanted to demonstrate their opposition to the Christian belief that the Temple Mount should remain empty. Moreover, the early Muslims may have had a spiritual attachment to the site before the conquest. Their utilization of the Temple Mount provided a vast space for the Muslims overlooking the whole city. The Temple Mount was likely used for Muslim prayer from the beginning of Muslim rule, due to the capitulation agreement's prohibitions on Muslims using Christian edifices. Such usage of the Temple Mount may have been authorized by Umar. The traditions cited by the 11th-century Jerusalemites al-Wasiti and Ibn al-Murajja note that Jews were employed as caretakers and cleaners of the Temple Mount and the ones employed were exempt from the jizya.
The earliest Muslim settlement activity took place south and southwest of the site, in thinly populated areas; much of the Christian settlement was concentrated in western Jerusalem around Golgotha
Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where Jesus was said to have been crucified according to the canonical Gospels. Since at least the early mediev ...
and Mount Zion
Mount Zion ( he, הַר צִיּוֹן, ''Har Ṣīyyōn''; ar, جبل صهيون, ''Jabal Sahyoun'') is a hill in Jerusalem, located just outside the walls of the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City. The term Mount Zion has been used in the Hebrew ...
. The first Muslim settlers in Jerusalem hailed mainly from the Ansar, i.e. the people of Medina. They included Shaddad ibn Aws, nephew of the prominent companion of Muhammad and poet Hassan ibn Thabit
Ḥassān ibn Thābit ( ar, حسان بن ثابت) (born c. 563, Medina died 674) was an Arabian poet and one of the Sahaba, or companions of Muhammad, hence he was best known for his poems in defense of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
He was b ...
. Shaddad died and was buried in Jerusalem between 662 and 679. His family remained prominent there, and his tomb later became a place of veneration. Another prominent companion, the Ansarite commander Ubada ibn al-Samit
'Ubadah ibn al-Samit ( ar, عبادة بن الصامت ) was a companion of Muhammad and a well-respected chieftain of the Ansar tribes confederation. He participated in almost every battle during Muhammad's era. His official title, according t ...
, also settled in Jerusalem where he became the city's first qadi
A qāḍī ( ar, قاضي, Qāḍī; otherwise transliterated as qazi, cadi, kadi, or kazi) is the magistrate or judge of a '' sharīʿa'' court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and mino ...
(Islamic judge). The father of Muhammad's Jewish concubine Rayhana and a Jewish convert from Medina, Sham'un (Simon), settled in Jerusalem and, according to Mujir al-Din, delivered Muslim sermons on the Temple Mount. Umm al-Darda
Umm al-Darda al-Kubra (Arabic: أم الدرداء الكبرى) was a companion of prophet Muhammad. She was a prominent jurist during the 7th century in Damascus.
One of her students, ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān, was the 5th Umayyad caliph. He s ...
, an Ansarite and the wife of the first qadi of Damascus, resided in Jerusalem for half of the year. Umar's successor Caliph Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic proph ...
() was said by the 10th-century Jerusalemite geographer al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
to have earmarked the revenues of Silwan
Silwan or Siloam ( ar, سلوان, translit=Silwan; gr, Σιλωὰμ, translit=Siloam; he, כְּפַר הַשִּׁילוֹחַ, translit=''Kfar ha-Shiloaḥ'') is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outski ...
's bountiful vegetable gardens on the city's outskirts, which would have been Muslim property per the capitulation terms, to the city's poor.
Umayyad period (661–750)
Sufyanid period (661–684)
CaliphMu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
(), the founder of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, originally served as the governor of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
under Umar and Uthman. He opposed Uthman's successor Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
during the First Muslim Civi War and forged a pact against him with the former governor of Egypt and conqueror of Palestine, Amr ibn al-As, in Jerusalem in 658.
According to the near-contemporary ''Maronite Chronicle
The ''Maronite Chronicle'' is an anonymous annalistic chronicle in the Syriac language completed shortly after 664. It is so named because its author appears to have been a Maronite. It survives today only in a single damaged 8th- or 9th-century m ...
'' and Islamic traditional accounts, Mu'awiya obtained oaths of allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For ...
as caliph in Jerusalem on at least two different occasions between 660 and July 661. Although the precise dating is inconsistent, the Muslim and non-Muslim accounts generally agree that the oaths to Mu'awiya took place at a mosque on the Temple Mount. The mosque may have been erected by Umar and expanded by Mu'awiya, though there are no apparent traces of the structure today. The ''Maronite Chronicle'' notes that "many emirs and Tayyaye rab nomadsgathered t Jerusalemand proffered their right hand to Mu'awiya". Afterward, he sat and prayed at Golgotha and then prayed at Mary's Tomb
; hy, Սուրբ Մարիամ Աստվածածնի գերեզման), is a Christian tomb in the Kidron Valley – at the foot of Mount of Olives, in Jerusalem – believed by Eastern Christians to be the burial place of Mary, the mother of Jesus ...
in Gethsemane
Gethsemane () is a garden at the foot of the Mount of Olives in Jerusalem where, according to the four Gospels of the New Testament, Jesus underwent the agony in the garden and was arrested before his crucifixion. It is a place of great resona ...
. The "Arab nomads" were likely the indigenous Arab tribesmen of Syria, most of whom had converted to Christianity under the Byzantines and many of whom had retained their Christian faith during the early decades of Islamic rule. Mu'awiya's prayer at Christian sites was out of respect for the Syrian Arabs, who were the foundation of his power. His advisers Sarjun ibn Mansur and Ubayd Allah ibn Aws the Ghassanid
The Ghassanids ( ar, الغساسنة, translit=al-Ġasāsina, also Banu Ghassān (, romanized as: ), also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom. They emigrated from southern Arabia in the early 3rd century to the Levan ...
may have helped organize the Jerusalem ceremonies.
Mu'awiya's son and successor to the caliphate, Yazid I
Yazid ibn Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan ( ar, يزيد بن معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Yazīd ibn Muʿāwiya ibn ʾAbī Sufyān; 64611 November 683), commonly known as Yazid I, was the second caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate. He ruled from ...
(), may have visited Jerusalem on several occasions during his lifetime. The historian Irfan Shahid
In Islam, ‘Irfan (Arabic/Persian/Urdu: ; tr, İrfan), literally ‘knowledge, awareness, wisdom’, is gnosis. Islamic mysticism can be considered as a vast range that engulfs theoretical and practical and conventional mysticism, but the c ...
theorizes that the visits, in the company of the prominent Arab Christian poet al-Akhtal
Ghiyath ibn Ghawth ibn al-Salt ibn Tariqa al-Taghlibi () commonly known as al-Akhtal () (The Loquacious), was one of the most famous Arab poets of the Umayyad period. He belonged to the Banu Taghlib tribe, and was, like his fellow-tribesmen, a Ch ...
, were attempts to promote his own legitimacy as caliph among the Muslims.
Marwanid period (684–750)
Marwan I
Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya ( ar, links=no, مروان بن الحكم بن أبي العاص بن أمية, Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam ibn Abī al-ʿĀṣ ibn Umayya), commonly known as MarwanI (623 or 626April/May 685), was the fo ...
(), received his oaths of allegiance in Jerusalem. From the beginning of his caliphate, Abd al-Malik began plans for the construction of the Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
and the al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situate ...
, both located on the Temple Mount. The Dome of the Rock was completed in 691–692, constituting the first great work of Islamic architecture. The Dome of the Rock's construction was supervised by the Caliph's theological adviser Raja ibn Haywa
Rajaʾ ibn Ḥaywa ibn Khanzal al-Kindī () was a prominent Muslim theological and political adviser of the Umayyad caliphs Abd al-Malik (), al-Walid I (), Sulayman () and Umar II (). He was a staunch defender of the religious conduct of the cali ...
of Beisan and his Jerusalemite ''mawla
Mawlā ( ar, مَوْلَى, plural ''mawālī'' ()), is a polysemous Arabic word, whose meaning varied in different periods and contexts.A.J. Wensinck, Encyclopedia of Islam 2nd ed, Brill. "Mawlā", vol. 6, p. 874.
Before the Islamic prophet ...
'' (non-Arab convert to Islam) Yazid ibn Salam. The construction of the Dome of the Chain
Dome of the Chain ( ar, قبة السلسلة, Qubbat al-Silsilah) is an Islamic free-standing domed building located adjacently east of the Dome of the Rock in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is one of many small buildings that can be found scatte ...
on the Temple Mount is generally credited to Abd al-Malik.
Abd al-Malik and his practical viceroy over Iraq, al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf
Abu Muhammad al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi Aqil al-Thaqafi ( ar, أبو محمد الحجاج بن يوسف بن الحكم بن أبي عقيل الثقفي, Abū Muḥammad al-Ḥajjāj ibn Yūsuf ibn al-Ḥakam ibn Abī ʿAqīl al-T ...
, are credited by the Islamic tradition for constructing two gates of the Temple Mount, which Elad proposes are the Prophet's Gate and the Mercy Gate; both are attributed to the Umayyads by modern scholars. The Caliph repaired the roads connecting his capital Damascus with Palestine and linking Jerusalem to its eastern and western hinterlands. The roadworks are evidenced by seven milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway line, canal or boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks; or they can give their position on the route relative to so ...
s found throughout the region, the oldest of which dates to May 692 and the latest to September 704. The milestones, all containing inscriptions crediting Abd al-Malik, were found, from north to south, in or near Fiq, Samakh, St. George's Monastery of Wadi Qelt, Khan al-Hathrura, Bab al-Wad and Abu Ghosh. The fragment of an eighth milestone, likely produced soon after Abd al-Malik's death, was found at Ein Hemed
Ein Hemed is a national park and nature reserve in the hills seven kilometres west of modern Jerusalem and some 12 kilometres west of the Old City. It is also known by the Latin name it received from the Crusaders, Aqua Bella, and as Khirbat Iq ...
, immediately west of Abu Ghosh. The road project formed part of the Caliph's centralization drive, special attention being paid to Palestine due to its critical position as a transit zone between Syria and Egypt and Jerusalem's religious centrality to the Caliph.
Extensive building works took place on the Temple Mount and outside of its walls under Abd al-Malik's son and successor al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ( ar, الوليد بن عبد الملك بن مروان, al-Walīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān; ), commonly known as al-Walid I ( ar, الوليد الأول), was the sixth Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad ca ...
(). Modern historians generally credit al-Walid with the construction of the al-Aqsa Mosque on the Temple Mount, though the mosque may have been originally built by his Umayyad predecessors; according to the latter view, al-Walid was nonetheless responsible for part of the mosque's construction. The Aphrodito Papyri indicate that laborers from Egypt were sent to Jerusalem for terms ranging between six months and one year to work on the al-Aqsa Mosque, al-Walid's caliphal palace, and a third, undefined building for the Caliph. Elad holds that the six Umayyad buildings excavated south and west of the Temple Mount may include the palace and undefined building mentioned in the papyri.
Al-Walid's brother and successor Sulayman
Sulayman (Arabic: سُلِيمَان ''sulaymān'') is an Arabic name of the Biblical king and Islamic prophet Solomon meaning "man of peace", derived from the Hebrew name Shlomo.
The name Sulayman is a diminutive of the name Salman (سَلْ ...
(), who had served as the governor of Jund Filastin under al-Walid and Abd al-Malik, was initially recognized as caliph in Jerusalem by the Arab tribes and dignitaries. He resided in Jerusalem for an unspecified period during his caliphate, and his contemporary, the poet al-Farazdaq
Hammam ibn Ghalib ( ar, همام بن غالب; born c. 641; died 728–730), most commonly known as Al-Farazdaq () or Abu Firas, was an Arab poet.
He was born in, Kazma. He was a member of Darim, one of the most respected divisions of the Bani T ...
, may have alluded to this in the verse "In the Mosque al-Aqsa resides the Imam ulayman. He constructed a bathhouse there, but may not have shared the same adoration for Jerusalem as his predecessors. Sulayman's construction of a new city, Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, located about northwest of Jerusalem, came at Jerusalem's expense in the long-term, as Ramla developed into Jund Filastin's administrative and economic capital.
According to the Byzantine historian Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking u ...
(d. 818), Jerusalem's walls were destroyed by the last Umayyad caliph, Marwan II
Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam ( ar, مروان بن محمد بن مروان بن الحكم, Marwān ibn Muḥammad ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; – 6 August 750), commonly known as Marwan II, was the fourteenth and last caliph of ...
, in 745. At that time, the Caliph had suppressed the Arab tribes in Palestine opposed to him for joining the revolt of the Umayyad prince Sulayman ibn Hisham
Sulaymān ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Malik (; ) was an Arab general, the son of the Umayyad Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik (). He is known for his participation in the expeditions against the Byzantine Empire as well as his prominent role in the civ ...
in northern Syria.
Muslim pilgrimage and rituals in the Umayyad period
Under the Umayyads the focus of Muslim ritual ceremonies and pilgrimage in Jerusalem was the Temple Mount and to a lesser extent the Prayer Niche of David (possibly theTower of David
The Tower of David ( he, מגדל דוד, Migdál Davíd), also known as the Citadel ( ar, القلعة, al-Qala'a), is an ancient citadel located near the Jaffa Gate entrance to the Old City of Jerusalem.
The citadel that stands today dates t ...
), the Spring of Silwan
Silwan or Siloam ( ar, سلوان, translit=Silwan; gr, Σιλωὰμ, translit=Siloam; he, כְּפַר הַשִּׁילוֹחַ, translit=''Kfar ha-Shiloaḥ'') is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outski ...
, the Garden of Gethsemane and Mary's Tomb, and the Mount of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet ( he, הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; ar, جبل الزيتون, Jabal az-Zaytūn; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jeru ...
. The Umayyads encouraged Muslim pilgrimage and prayer in Jerusalem and traditions originated during the Umayyad period celebrated the city. During this period, Muslim pilgrims came to Jerusalem to sanctify themselves before making the Umra or Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried ...
pilgrimages to Mecca. Muslims who could not make the pilgrimage, and possibly Christians and Jews, donated olive oil for the illumination of the al-Aqsa Mosque. The bulk of the Muslim pilgrims to Jerusalem were presumably from Palestine and Syria in general, though several came from distant parts of the Caliphate.
Abbasids, Tulunids and Ikhshidids (750–969)
The Umayyads were toppled in 750 by theAbbasid dynasty
The Abbasid dynasty or Abbasids ( ar, بنو العباس, Banu al-ʿAbbās) were an Arab dynasty that ruled the Abbasid Caliphate between 750 and 1258. They were from the Qurayshi Hashimid clan of Banu Abbas, descended from Abbas ibn Abd al-M ...
, which afterward ruled the Caliphate including Jerusalem, with interruptions, for the next two centuries. This period is the least documented of the early Muslim period in general. Known building activity was concentrated in the Temple Mount area and was characterized by repairs of structures damaged in earthqauakes. The caliphs al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ar, أبو جعفر عبد الله بن محمد المنصور; 95 AH – 158 AH/714 CE – 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manṣūr (المنصور) w ...
() and al-Mahdi
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Manṣūr ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد بن عبد الله المنصور; 744 or 745 – 785), better known by his regnal name Al-Mahdī (, "He who is guided by God"), was the third Abba ...
() ordered major reconstruction of the al-Aqsa Mosque after earthquake damage.
After the first Abbasid period (750–878), the Tulunids
The Tulunids (), were a Mamluk dynasty of Turkic origin who were the first independent dynasty to rule Egypt, as well as much of Syria, since the Ptolemaic dynasty. They were independent from 868, when they broke away from the central authori ...
, a mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
dynasty of Turkic origin, managed to independently rule over Egypt and much of Greater Syria, including Palestine, for almost three decades (878–905). Ahmad ibn Tulun
Ahmad ibn Tulun ( ar, أحمد بن طولون, translit=Aḥmad ibn Ṭūlūn; c. 20 September 835 – 10 May 884) was the founder of the Tulunid dynasty that ruled Egypt and Syria between 868 and 905. Originally a Turkic slave-soldier, in 868 ...
, the founder of the Egypt-based dynasty, consolidated his rule over Palestine between 878 and 880 and passed it on to his son at his death in 884. According to Patriarch Elias III of Jerusalem
Elias III was the Patriarch of Jerusalem from about 879 to 907.
According to the annals of Eutychius of Alexandria, he was a descendant of the family of Mansur ibn Sarjun, the grandfather of John of Damascus.
There is evidence that he sent a ci ...
, Ibn Tulun finished a period of persecution against Christians by naming a Christian governor in Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
(or perhaps Jerusalem), the governor initiating the renovation of churches in the city. Ibn Tulun had a Jewish physician and generally showed a very relaxed attitude towards ''dhimmi
' ( ar, ذمي ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligatio ...
s'', and when he lay on his deathbed, both Jews and Christians prayed for him. Ibn Tulun was the first in a line of Egypt-based rulers of Palestine, which ended with the Ikhshidids. While the Tulunids managed to preserve a high degree of autonomy, the Abbasids retook control over Jerusalem in 905, and between 935 and 969 it was administered by their Egyptian governors, the Ikhshidids. During this entire period, Jerusalem's religious importance grew, several of the Egyptian rulers choosing to be buried there.
Abbasid rule returned between 905 and 969, the first 30 years of which was direct rule from Baghdad (905–935), and the rest was through the Ikhshidid
The Ikhshidid dynasty (, ) was a Turkic mamluk dynasty who ruled Egypt and the Levant from 935 to 969. Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid, a Turkic mamluk soldier, was appointed governor by the Abbasid Caliph al-Radi. The dynasty carried the Arabic t ...
governors of Egypt (935–969). The mother of Caliph al-Muqtadir
Abu’l-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Ahmad al-Muʿtaḍid ( ar, أبو الفضل جعفر بن أحمد المعتضد) (895 – 31 October 932 AD), better known by his regnal name Al-Muqtadir bi-llāh ( ar, المقتدر بالله, "Mighty in God"), wa ...
() had wooden porches built under all the city gates and repaired the Dome of the Rock.
The Ikhshidid period was characterised by acts of persecution against the Christians, including an attack by the Muslims on the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in 937, with the church set on fire and its treasure robbed. The tensions were connected with the renewed threat posed by the encroaching Byzantines, and on this background the Jews joined forces with the Muslims. In 966 the Muslim and Jewish mob, instigated by the Ikhshidid governor, attacked again the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, the resulting fire causing the collapse of the dome standing over the Tomb of Jesus and causing the death of Patriarch John VII.
Fatimids and Seljuks (970–1099)
The start of the firstFatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dy ...
period (970–1071) saw a predominantly Berber army conquer the region. After six decades of war and another four of relative stability, Turkish tribes invade the region, starting off a period of permanent upheaval, fighting against each other and the Fatimids and, in less than thirty years of warfare and vandalism, destroyed much of Palestine, bringing terrible hardships, particularly on the Jewish population. However, the Jewish communities stayed in their places, only to be uprooted after 1099 by the Crusaders. Turkish rule totalled more than a quarter of a century of constant warfare, negatively affecting the local Christian communities, as well as eventually blocking the access of pilgrims from Europe, which is seen as a factor in initiating the Crusades. We know however also about a visitor from Muslim Spain, who left us a report about the intense activity in Jerusalem's Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
s and his interaction with Jews and Christians in the years 1093–95.
Between 1071 and 1076, Palestine was captured by Turkman or Turcoman tribes, with Jerusalem falling in 1073. The Turcomans acted in the region as free agents, but became known as Seljuqs, after the primary rulers among the Turkish invaders of the Arab Muslim realm, the Seljuk dynasty
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, whom they were associated with. Seljuk emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
Atsiz ibn Uvaq
Atsiz ibn Uwaq al-Khwarizmi, also known as al-Aqsis, Atsiz ibn Uvaq, Atsiz ibn Oq and Atsiz ibn Abaq (died October 1079), was a Khwarezmian Turkish mercenary commander who established a principality in Palestine and southern Syria after seizing ...
al-Khwarizmi, leader of the Turkic tribe of the Nawaki, besieged and captured Jerusalem in 1073 and held it for four years. Atsiz placed the territory he captured under the nominal control of the 'Abbasid caliphate. In 1077, on his return from a disastrous attempt to capture Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, the capital of the Fatimid caliphate, he found that in his absence the inhabitants of Jerusalem had rebelled and forced his garrison to shelter in the citadel, capturing the families and property of the Turcomans.Gil (1997), p. 412. Atsiz besieged Jerusalem and promised the defenders the ''aman'', pardon and safety, at which they surrendered. Atsiz broke his promise and slaughtered 3000 inhabitants, including those who had taken shelter in the Al-Aqsa Mosque and only sparing those inside the Dome of the Rock. In 1079, Atsiz was murdered by his nominal ally Tutush
Abu Sa'id Taj al-Dawla Tutush (; died 25 February 1095) or Tutush I, was the Seljuk emir of Damascus from 1078 to 1092, and sultan of Damascus from 1092 to 1094.
Years under Malik Shah
Tutush was a brother of the Seljuk sultan Malik-Shah I. In 1 ...
, who subsequently established firmer 'Abbasid authority in the area. After Atsiz other Seljuk commanders ruled over Jerusalem and used it as a power base in their unceasing wars. A new period of turbulence began in 1091 with the death of Tutush's governor in Jerusalem, Artuq and the succession of his two sons, who were bitter rivals. The city changed hands between them several times, until August 1098, when the Fatimids, seizing the opportunity presented by the approach of the First Crusade, regained control of the city and ruled it for a less than a year.
Jewish community in the 11th century
The Jewish population suffered great hardship during the tumultuous years of Turkish rule, even the Jerusalem ''yeshiva'', the central institution of Jewish law in Palestine, being forced to move to Tyre sometime after 1078, in the wake of the rebellion against Atsiz, although there is no information on whether the Jews did take part in it along with the Muslim citizens. According to Rabbi Elijah of Chelm,German Jews
The history of the Jews in Germany goes back at least to the year 321, and continued through the Early Middle Ages (5th to 10th centuries CE) and High Middle Ages (''circa'' 1000–1299 CE) when Jewish immigrants founded the Ashkenazi Jewish ...
lived in Jerusalem during the 11th century. The story is told that a German-speaking Palestinian Jew saved the life of a young German man surnamed Dolberger. So when the knights of the First Crusade came to besiege Jerusalem, one of Dolberger's family members who was among them rescued Jews in Palestine and carried them back to Worms Worms may refer to:
*Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs
Places
*Worms, Germany, a city
**Worms (electoral district)
*Worms, Nebraska, U.S.
*Worms im Veltlintal, the German name for Bormio, Italy
Arts and entertainme ...
to repay the favor. Further evidence of German Jewish communities in the holy city comes in the form of halakic
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical command ...
questions sent from Germany to Jerusalem during the second half of the 11th century.Epstein, in "Monatsschrift", xlvii. 344Jerusalem: Under the Arabs
/ref>
Christian community in the 11th century
As the Byzantine borders expanded into the Levant in the early 11th century, the limited tolerance of the Muslim rulers toward Christians in the Middle East, began to wane. TheEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
ian Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dy ...
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Abū ʿAlī Manṣūr (13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh ( ar, الحاكم بأمر الله, lit=The Ruler by the Order of God), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili ima ...
ordered the destruction of all churches throughout the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
starting with those in Jerusalem. The Church of the Holy Resurrection, revered by all Christians of the time as the site of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, names and titles), was ...
's crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the victim is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross or beam and left to hang until eventual death from exhaustion and asphyxiation. It was used as a punishment by the Persians, Carthagin ...
and burial
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
, was among the places of worship destroyed, but permission was later given for its rebuilding.
The suffering and privation caused by the decades of bellicose Turkish rule lead some local Christians to expect the imminent coming of the End of Days, and as a consequence of the permanent war footing, the mainly Fatimid-held ports of Palestine turned away the pilgrims' ships arriving from Europe in 1093, a situation which contributed to the start of the First Crusade. Altogether, although information is very scarce, it seems that the Turcomans favoured the Jacobites
Jacobite means follower of Jacob or James. Jacobite may refer to:
Religion
* Jacobites, followers of Saint Jacob Baradaeus (died 578). Churches in the Jacobite tradition and sometimes called Jacobite include:
** Syriac Orthodox Church, sometime ...
and Latins
The Latins were originally an Italic tribe in ancient central Italy from Latium. As Roman power and colonization spread Latin culture during the Roman Republic.
Latins culturally "Romanized" or "Latinized" the rest of Italy, and the word Latin ...
over the Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek language, Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the Eastern Orthodox Church, entire body of Orthodox (Chalced ...
, who were seen as close to the Byzantine Empire, a constant enemy.
See also
* Islamization of JerusalemReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*{{cite book , editor1-last=Prawer , editor1-first=Joshua , editor2-last=Ben-Shammai , editor2-first=Haggai , title=The History of Jerusalem: The Early Muslim Period (638-1099) , date=1996 , publisher=Yad Izhak Ben Zvi and New York University Press , isbn=0-8147-6639-0 , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-qQUCgAAQBAJ Medieval Jerusalem